Nowadays there is tracked the strengthening of positions of institutional economic theory at the macro- and microeconomic level. Obedience or expressed by the individuals agreement to obey the determined limits promote the realization of institutional requirements at the conomic activity of subjects[1].
«The rule, which was institutionalized, is identified with the institute»[2], - there state J.-E. Lain and S. Ersson. Consequently, every economic subject has peculiar inside functional and cultural microinstitution, as the account policy. The complex of special chosen normative-legal rules, organizationally-technical norms, traditions, including traditions of relations and coordinations of account activity of its personnel, concerning them legitimacy, are unique for the economic subject.
From the position of institutional conception the forming of account policy as the system of inside normative documents, which regulate bookkeeping (financial, tax, administrative) account, promotes more effective use of possibilities of every system, which fits into conditions of active institutional sphere. The priority meaning for institutionalization of account policy of economic subject has the government (the influence is carried out through the normative acts by the questions of accounting and taxation), which should provide full correspondence of accounting and taxation to the action of market mechanism and creation for it the adequate conditions.
The institutionalization of account policy of economic subject means:
- the process of creation of the immanent organizationally-methodological institute, which provide the ordered functional structure with the hierarchy of power and rules of behavior while the presence of the stable differentiation of labour;
- the formation of defined rules and norms of methodology of account;
- the development and explanation of effective ways and methods, which are not foreseen by the legislation.
The necessity of research of modern mechanism of institutionalization of account policy is conditioned by the needs of opening of organizational account system by the way of introduction of institutional norms into the vital functions of economic subjects. In compliance with such approach there is presented as the possible to single out the blocks of institutionalization of account policy, which are represented at the Figure: forming of norms and rules; interiorization of formal legal norms and rules of the «game»; realization of account policy and control of observance of the stated norms and rules; correction of norms and rules.
Forming of account policy (norms and rules). At the base of principles, rules and norms into the building of system of account of economic subject there are established the limits, which there is necessary to obey while the choice of the account ways, procedures and regulation of the account process. The account policy of organization for the aims of accounting should answer to the principle of integrity of the accounting and include following aspects: organizational; technical; methodological.
Interiorization of formal legal norms and rules of the «game». «Interiorization (passage from without to inside) is the process, the base task of which is introduction of new institutions into the routine activity of different subjects»[3]. The introduction of such microinstitution as the account policy requires the creation of defined standards of behavior of account personnel. Inside acceptance of the generally used professional principles means the making of the correspondent personality qualities of specialists, which are necessary for the regulation of behavior while reaching the decision, when choice is necessary. The standing of account policy promotes the consolidation of personnel of bookkeeping service of economic subject for the solving of problems of account from the view of carrying out of their professional activity in compliance with requirements, which are brought by government institutions.
Realization of the account policy and observance of stated norms and rules control The realization of the formed account policy is connected with the practical realization of bookkeeping and tax account, conclusion of the treaties. Established totality of norms and rules at the account policy while its realization should provide maximal result from the accounting dependending on the stated aims, to lower the bookkeeping and tax risks.
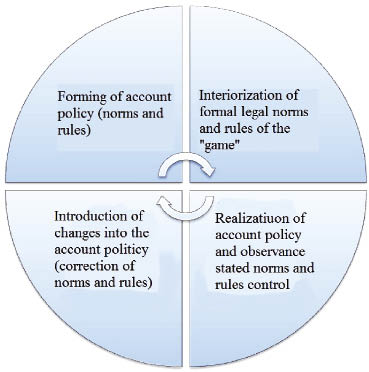
The mechanism of institutionalization of account policy
The organization of inside control, which is regulated by the standings of the account policy, with taking into consideration of accumulated experience and formed traditions provides the observance of the legislation at the sphere of accounting and taxation, requirements of account policy, including contractual.
Introduction of changes into the account policy (correction of norms and rules). The changes of account policy are carried out in cases: of change of legislation of RF or normative acts by the accounting; developments by the economic subject of new ways of carrying out of accounting (more reliable presentation of the facts of economic life or less laboriousness of account process without lowering of the degree of reliability of information); essential changes of activity conditions.
Corresponding to the p. 9 RAS 1/2008 «Account policy of organization» new rules should be used from the beginning of the year, because their different use should lead to the incommensurability of the facts of accountability. While the choice or development of the new ways of accounting, which were not earlier carried out by the economic subjects, they should be examined as addition, but not change of account policy. Then such ways of accounting should be used from the moment of their affirmation, but not from the further year.
The decision of introduction of changes into the account policy for the aims of taxation while the change of used methods of accounting is accepted from the beginning of the new tax period, and while the change of legislation of taxes and collection not earlier than from the moment of the carrying into of changes of norms of stated legislation[4].
Thereby, the institutional mechanism of account policy as the instrument provides the functioning of account system in compliance with stated norms and rules, and guarantees the reproduction of the stated (formed) institution of the account policy.
Modern paradigm of basic directions at the studying of the in-house institutionalizm od account policy is based on:
- degree of motivation of institutionalization of account policy from the view point of transaction costs;
- effectiveness of distribution of laws of property;
- effectiveness of contrast relations.
A.E. Shastitko gives following definition of the transaction costs: «Transation costs are the costs of resources (means, time, labour etc) for planning, adaptation and control of the carrying out of the taken by individual obligations at the process of alienation and appropriation of rights of property and freedom, which are accepted in the society»[5]. At the normative regulative by the accounting and in the taxing of RF there is no concept «transaction costs». By its essence the transaction costs are close to the costs of circulation, which were singled out by K. Marks. With the costs of production he also analyzed «the costs, which are necessary for that to turn costs from the commodity form into money one»[6]. While the examination of the process of forming of account policy there should be revealed the costs of reaching of decisions, which serve for reaching the optimum, to the bookkeeping, taxation, at the choice of type of concluded treaties and their defined conditions, which by their essence can be positioned as inside transaction costs.
One of the assumption, at the base of which there is based the account policy of economic subject, is property isolation. This assumption postulates the right of property of economic subject of the belongings. According to the paragraph 1 of the article 209 CC RGF to the owner there belongs the right of owing and order of their property. Financially-economic activity of economic subjects means not only distribution of the rights of property on the belongings but also rise of ration direction responsibility, forming and effective use of financial resources.
The results of financially-economic activity reflect the effectiveness of distribution of the rights of property, at the result of which any act of exchange by competence is carried out in the limits of concluded contracts (treaty policy). It gives a possibility to approach to the institutionalization of the account policy from the position of treaty regulating of the processes of exchange of rights and realization of economic interests.
At the most complicated system of property the contract relations are inalienable, the most important component. The admission of alternative of contract interaction of economic subjects results from the structure of property rights. At the frames of contract the economic interests of subjects of management there take a form of legally meaningful rights and obligations in compliance with treaty policy.
The creation of institution of account policy is the consequence of the process of institutionalization. Which characterize new qualitative level of standardization of account at the economic subject.
References
- Civil code of RF.
- Tax code of RF.
- Order of Minister of Finance of RF 6 of October 2008y. N 106n «About statement of the Standing by the accounting «Accounting policy of organization» RAS 1/2008.
- Istomin S.V. The peculiarities of institutional mechanisms at the transformed economy// The herald of Chelyabinsk state university. - 2010. - №6. - P. 52-56.
- Lebedeva N.N. Institutional mechanism: contents, structure, functions. // Economic magazine. - 2002. -№4. - P. 47-56.
- Marks K. The critic of political economy. V. 2. B. 2, The process of circulation of capital - M.: Politizdat, 1988.
- Williamson O.I. Economic institutions of capitalism: Companies, markets, «relational» contracting / Scientific redaction and introductory article V. S. Katkalo. - St. Petersburg: Lenizdat: CEV Press, 1996.
- Shastitko A.E. Institutional economy: theory and methodology: The dissertation of doctor of economic sciences . - M.: publishing office MGU, 1999.
- Lane J-E., Ersson S. The new institutional politics: Performance and outcomes. - L.-N.Y.: Routledge, 2000.
[1] Williamson O.I. Economic institutions of capitalism: Companies, markets, «relational» contracting / Scientific redaction and introductory article V. S. Katkalo. St. Petersburg: Lenizdat: CEV Press, 1996. P. 100-101.
[2] Lane J-E., Ersson S. The new institutional politics: Performance and outcomes. - L.-N.Y.: Routledge, 2000. P.3.
[3] Istomin S.V. The peculiarities of institutional mechanisms at the transformed economy// The herald of Chelyabinsk state university. - 2010. - N6. - P. 54.
[4] Indentation 6 article 313 TC RF.
[5] Shastitko A.E. Institutional economy: theory and methodology: The dissertation of doctor of economic sciences . - Moscow: publishing office MGU, 1999, p.119.
[6] arks K. The critic of political economy. V. 2.B. 2, The process of circulation of capital - M.: Politizdat, 1988, P. 151.

