Introduction
Insurance is a system of economic relations that includes a set of forms and methods of forming trust funds of funds used to protect the property and other interests of individuals, legal entities and the state in the event of certain events [1].
Medical insurance is a form of social protection of the interests of the population in health protection, the purpose of which is, in the event of an insured event, guaranteed receipt of medical care by citizens at the expense of accumulated funds, as well as financing of preventive measures. Medical insurance is carried out in two types: mandatory and voluntary and is an important part of the social protection of the population.
Voluntary medical insurance (VMI) includes additional services that are not included in the mandatory medical insurance programs, can be individual and intended for legal entities – corporate. Voluntary medical insurance appeared in Russia in 1991 after the adoption of the Law of the RSFSR of 28.06.1991 No. 1499-1 “On medical insurance of citizens in the RSFSR” [2] and continues to exist to this day, adjacent to mandatory medical insurance. The main reason for the emergence and existence of VMI is the demand of policyholders and insured persons for an expanded and high-quality volume of medical services, and the provision of tax benefits to both individuals and legal entities who have sent their funds to health funds by purchasing policies of this type of insurance is a significant fiscal support [3].
The purpose of the study, materials and methods
The purpose of this work is an analytical review of statistical data reflecting the indicators of voluntary medical insurance according to various criteria, as well as using the expert assessment method to identify the positive and negative aspects of this type of insurance. The relevance of the study is due to the fact that voluntary medical insurance, especially its corporate component, is a growing segment of the insurance market and is the most popular type of insurance in Russia, which is confirmed by statistical data and scientific publications.
Results and discussions
If we consider the official statistics, the top five leaders in voluntary health insurance among the regions, presented in Table 1, looks like this:
Table 1
Distribution of LCA receipts by cumulative total by regions for 12 months of 2020
|
No |
Dynamics from 2019. |
Region |
Cumulative total receipts |
|
|
thousand rubles |
% of the total market |
|||
|
1. |
|
Moscow |
99 636 228 |
56,3 % |
|
2. |
|
Saint-Petersburg |
39 244 365 |
22,18 % |
|
3. |
|
Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug – Yugra |
4 584 370 |
2,59 % |
|
4. |
|
Sverdlovsk region |
2 774 854 |
1,57 % |
|
5. |
|
Republic of Tatarstan |
2 221 118 |
1,26 % |
|
|
Other regions |
28 503 793 |
16,1 % |
|
Source: Compiled by the author on the basis of data [4].
Moscow leads by a significant margin with revenues of 56.3 % of the entire market, followed by St. Petersburg – 22.18 %, the other regions are significantly behind. Thus, the provision of VMI services is concentrated in two capitals of Russia. This fact is due to the low income of the population living in the regions, since it is in the regions that for many years there has been an increase in the share of the population whose income is below the subsistence minimum, and the cost of a voluntary health insurance policy is quite high. Also, all the leading insurance companies are concentrated in Moscow, due to the convenience of doing business and the availability of solvent customers, that is, the emphasis is on making a profit by insurers.
Table 2 shows the dynamics of fees and payments under the VMI for 2011-2020, indicating percentages from previous periods and payment coefficients.
Figure 1 clearly demonstrates the increase in fees and payments for VMI for 2011-2019. Thus, there is a constant increase in cash receipts for programs, as well as an increase in payments for insurance cases. However, the 2020 pandemic made adjustments in all spheres of society, and voluntary health insurance was no exception – the indicators decreased. In this regard, it will be interesting to analyze the data for 2021-2022 in the future.
Table 2
Dynamics of VMI fees and payments for 2011-2020
|
Year |
|
|
Payout coefficient % |
||
|
Receipts (thousand rubles) |
% of the previous year’s indicator |
Payments (thousand rubles) |
% of the previous year’s indicator |
||
|
2020 |
176 964 713 |
97,96 |
118 206 690 |
93,45 |
66,80 |
|
2019 |
180 654 783 |
118,97 |
126 495 453 |
113,01 |
70,02 |
|
2018 |
151 843 113 |
108,45 |
111 930 614 |
105,78 |
73,71 |
|
2017 |
140 007 952 |
101,59 |
105 811 237 |
105,14 |
75,58 |
|
2016 |
137 816 419 |
106,87 |
100 634 322 |
101,00 |
73,02 |
|
2015 |
128 956 970 |
103,94 |
99 641 322 |
104,64 |
77,27 |
|
2014 |
124 074 582 |
107,92 |
95 219 627 |
105,87 |
76,74 |
|
2013 |
114 965 640 |
105,81 |
89 941 540 |
110,29 |
78,23 |
|
2012 |
108 653 999 |
111,80 |
81 551 462 |
111,01 |
75,06 |
|
2011 |
97 183 789 |
113,32 |
73 463 178 |
111,84 |
75,59 |
Source: [4].
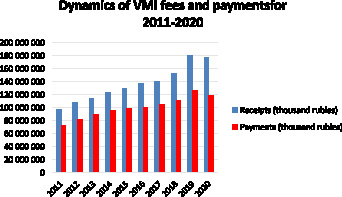
Fig. 1. Dynamics of VMI fees and payments for 2011-2020 Source: Compiled by the author on the basis of data from Table 2
Figure 2 shows the coefficient of payments under the VMI for 2011-2020.
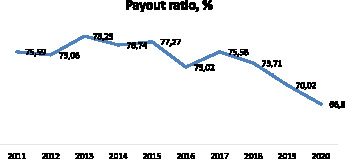
Fig. 2. The coefficient of payments under the VMI for 2011-2020. Source: Compiled by the author on the basis of data from Table 2
Table 3
Dynamics of VMI fees and payments for 12 months of 2020: TOP-5 insurance companies
|
No |
Name, city |
|
|
Payout ratio |
||||
|
Place in the ranking |
Receipts (thousand rubles) |
% of the previous year’s indicators |
Place in the ranking |
Payments (thousand rubles) |
% of the previous year’s indicators |
|||
|
1. |
JSC “SOGAZ” Moscow |
1 |
64 352 886 |
106,82 |
1 |
48 575 248 |
92,30 |
75,48 |
|
2. |
Insurance PJSC “RESO-Garantia” Moscow |
2 |
20 062 545 |
114,29 |
2 |
14 422 341 |
106,07 |
71,89 |
|
3. |
JSC “AlfaStrakhovanie” Moscow |
3 |
17 857 463 |
116,28 |
3 |
11 887 131 |
106,10 |
66,57 |
|
4. |
PJSC IC “Rosgos-strakh” Moscow |
4 |
12 187 276 |
61,88 |
5 |
5 752 583 |
94,55 |
47,20 |
|
5. |
Insurance PJSC “Ingosstrakh” Moscow |
5 |
9 556 485 |
87,75 |
4 |
6 802 557 |
81,22 |
71,18 |
Source: Compiled by the author on the basis of data [4].
It should be noted that the variation of the indicators presented in Figure 2 cannot be associated with external factors, but only with internal factors that directly affect this coefficient: the number of requests for medical care, the type of medical care and the cost of services provided.
The growth in the number of contracts concluded and the steady volume of the VMI market in monetary terms indicate a continued increase in the volume of this type of insurance. Both receipts and payments are growing. This conclusion is made without taking into account the consequences caused by the pandemic, since positive dynamics was demonstrated throughout the entire study period before its occurrence. And we are confident that after overcoming the difficulties caused by the pandemic, the VMI market will continue its intensive development.
In accordance with the statistical data, we will conduct an analysis of the leading LCA insurers in the insurance market (Table 3).
The undisputed leader in the market of insurance services for voluntary medical insurance is JSC “SOGAZ”, its indisputable advantages are presented in the figures of cash receipts, as well as payments for insured events. Thus, the insurance PJSC “RESO-Garantia” Moscow, which occupies the second place in the ranking in terms of receipts and payments, lags behind JSC “SOGAZ” by more than three times.
So, after considering some statistical indicators, we can conclude that, basically, the advantages that the VMI policy gives are enjoyed by residents of large cities working in prestigious companies, there is an increase in the number of contracts concluded, there is a constant increase in cash receipts for programs, and payments for insurance cases are also increasing. The leading insurance company providing services for voluntary medical insurance is JSC “SOGAZ”. The intensive development of the market, increased competition between insurance companies, medical institutions due to the improvement of the quality of service, the complication of the service component of insurance products leads to further concentration on the VMI market [5].
However, with the identified positive trends in the development of voluntary medical insurance, it is impossible not to mention the problems in this sector of insurance services, which can be divided into external and internal. We will not focus on the pandemic, since the problems caused by it are unconditional and have affected every sector of the economy. Figure 3 shows the classification of problems of voluntary health insurance by internal and external components.
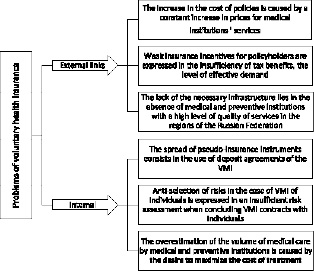
Fig. 3. Problems of voluntary health insurance Source: [6]
The main clients of insurance companies in terms of voluntary health insurance are corporate clients, they account for about 90 % of the contributions collected under these programs, this happens for a number of reasons, the main of which include the following:
● In recent years, the level of business involvement in solving social problems has significantly increased, including the provision of medical services to its employees and their family members.
● In addition to the growth of social responsibility of business, there is also an interest of insurance companies to work with corporate clients, due to the uniform distribution of risks among all insured employees and a high percentage of negative selection when concluding VHI contracts with individuals.
● Also, the low financial situation of the population does not make it possible to purchase a VMI policy privately, due to its high cost.
Thus, the main part of the VMI market falls on corporate clients and, for example, in Moscow and St. Petersburg, according to experts, 95 % is corporate. In the regions, companies that insure their employees prefer depository insurance and the use of VMI to finance their own medical unit or organize the treatment of employees in sanatoriums and dispensaries [1].
Investments in human capital are one of the crucial conditions for increasing the efficiency of any company, and VMI is one of the directions of such investments. The social package is understood as additional social benefits and guarantees to employees, and each employer provides it on its own initiative and on a voluntary basis, and it serves as a competitive advantage of the company. The social package may include medical care for employees, that is, a program of corporate voluntary medical insurance. Corporate VMI is a program of social guarantees in the medical field, including compensation for the costs of treatment, examination and hospitalization of the organization’s personnel.
Figure 4 shows the scheme of interaction of VMI subjects.
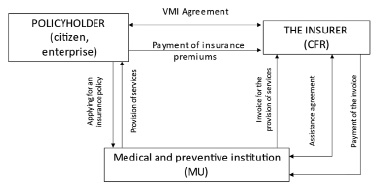
Fig. 4. Scheme of interaction of VMI subjects Source: [7]
In accordance with Article 157 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the VMI agreement is one of the conditional transactions. The policyholder has the right to demand payment of the insured amount from the insurer only from the moment of occurrence of the insured event. The insured event also has a feature inherent in a conditional transaction: the condition and the insured event are equally obligations with respect to which it is unknown whether they will occur or not [8].
The absolute advantages of voluntary health insurance for employees are:
● Additional free social guarantees;
● Getting medical care in the best medical institutions;
● The possibility of choosing a medical institution from the list offered by the insurance company;
● Full compensation of medical care costs;
● Qualified medical staff, polite and attentive;
● Individual approach;
● Reception by appointment at a convenient time, no queues;
● The possibility of calling a doctor at home or at work;
● Registration of sick leaves, certificates and other documents;
● Spa treatment (subject to inclusion in the program);
● The possibility of insuring family members.
The advantages for legal entities that insure their employees are:
● Getting tax benefits:
o In accordance with paragraph 16 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the maximum amount of contributions not exceeding 6 % of the total cost of salary payments under a VMI agreement concluded for at least 1 year can reduce the tax base for income tax [9];
o According to paragraph 1 of Article 238 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amounts of insurance premiums under the VMI contract, which was concluded for at least 1 year, are not subject to a single social tax [9];
o In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 213 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when calculating the tax base of an individual, the income that he receives as an insurance payment upon the occurrence of an insured event is not taken into account [9].
● Increasing the prestige of the organization and the loyalty of employees;
● Attracting qualified employees;
● Reducing the turnover of qualified personnel;
● Reducing the loss of working time and, accordingly, increasing labor productivity.
And others.
Thus, in addition to the main function of voluntary medical insurance – receiving highly qualified volume medical care, there are additional bonuses that confirm the benefits for both insured and insured persons, and it is this that is the main factor in the dynamic development of this type of insurance.
VMI programs include various types of medical care:
● Outpatient clinic;
● Stationary;
● Comprehensive;
● Special programs
In case of illness, you can seek help in two ways:
● Direct access (applying to a medical institution from the list provided by the insurance company);
● Access through the insurance company (round-the-clock phone number of the insurance company, confirmation of payment for the necessary service).
For corporate VMI, there are various schemes that are applied depending on the personnel belonging to different grades (Fig. 5).
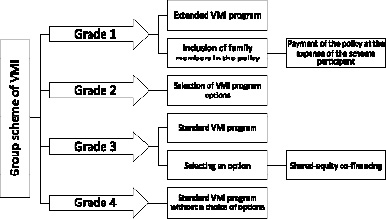
Fig. 5. Scheme of group insurance of VMI Source: [10]
The employer’s choice of a VMI program is influenced by many factors: the position of the employee, the length of service, the value of the employee for the company. For example, employees belonging to grade 3 can be insured under the standard VMI program, and elective options with the inclusion of shared co-financing can also be applied to this program. All the years of using VMI, the possibility of insuring relatives of employees of the company – grade 1 has become very popular. As a rule, the standard and extended VMI program does not include aesthetic medicine and cosmetology. The full VMI program, costing from 100,000 rubles, includes, in addition to the list included in the standard (basic) and extended programs, the following:
● Access to expensive private and public high-tech clinics;
● Expensive high-tech research;
● Hospitalization for emergency and planned indications in separate wards of Luxury clinics;
● Dental care, includes prosthetics and implantation;
● Pregnancy management and maternity care;
● Psychotherapy services;
● Diagnostics and treatment in foreign medical institutions
And so on.
If there are a large number of advantages of corporate voluntary medical insurance, the main disadvantage for employees is that the insurance program is chosen directly by the employer, the conditions are dictated by him. So, if the insured amount is exceeded per person under the collective insurance contract, the insured will have to pay for treatment independently. And with an extended VMI program, the employer may ask the employee to pay part of the insurance premium. However, with the existing disadvantages, a significant plus is that the cost of a corporate voluntary health insurance policy is significantly lower than a policy for an individual.
An important point for both corporate and private VMI is that unpaid medical services are mandatory prescribed in the insurance contract. It should be noted that if the client of the insurance company already has some serious diseases, such as:
● Oncological diseases;
● Dangerous infectious diseases;
● Venereal diseases;
● AIDS;
● Hepatitis;
● Tuberculosis;
● Diabetes mellitus;
● Mental disorders;
● Congenital chronic diseases;
● Complicated pregnancy;
● Infertility
and the patient will have a long-term treatment and rehabilitation, in this case, the insurance company may not conclude a VMI contract. If the concealment of the presence of a serious illness is detected, the insurance company has the right to terminate the insurance contract. Within the framework of VMI, chronic diseases are treated only in the acute stage if there is a threat to the patient’s life. If the above-mentioned diseases are detected during the examination of the patient, the insurance company will pay for all studies and procedures until the diagnosis is made.
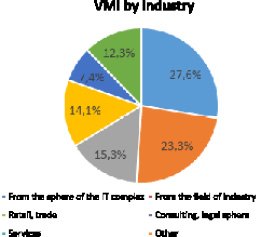
Fig. 6. VMI by industry Source: [11]
In accordance with the analytical review of the voluntary health insurance market prepared by AST Company:
● This type of corporate insurance is most in demand in raw materials companies and IT sector companies and accounts for 27.6 % (Fig. 6);
● The most popular options are outpatient consultations and inpatient care (Fig. 7);
● There is an increased popularity of options related to telemedicine, as well as a growing demand for coinage (Fig. 8);
● The success factors of the clinics are:
o Professional team;
o Modern methods of diagnosis and examination;
o Convenient location;
o Service;
o High places in the quality ratings compiled by the media.
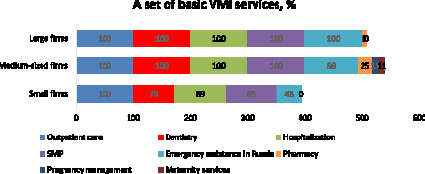
Fig. 7. A set of basic VMI services Source: [11]
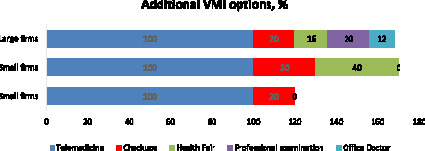
Fig. 8. Additional VMI options Source: [11]
Conclusion
Thus, voluntary medical insurance, especially its corporate component – is a growing segment of the insurance market and is the most popular type of insurance in Russia, which is confirmed by statistical data and scientific publications analyzed in the course of this study. The main part of the VMI market is accounted for by corporate clients, and in Moscow and St. Petersburg, 95 % is corporate. Investments in human capital are one of the crucial conditions for increasing the efficiency of any company, and VMI is one of the directions of such investments. This type of corporate insurance is most in demand in raw materials companies and companies in the IT sector, which is natural, since companies in these areas of activity are large businesses and are the most financially stable. And the cost of a corporate voluntary health insurance policy is significantly lower than the cost of a policy for an individual. The study identified the positive and negative aspects of the analyzed type of insurance.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the main advantage of corporate voluntary medical insurance for all participants of the scheme is the benefit expressed in different ways and it is this benefit that is the main factor in the dynamic development of this type of insurance.


_fmt.jpeg)
_fmt1.jpeg)
_fmt2.jpeg)
_fmt3.jpeg)
_fmt4.jpeg)
_fmt5.jpeg)
 Receipts
Receipts Payouts
Payouts Receipts
Receipts Payouts
Payouts

