Statement of the problem. Given the limited state financial resources, the problem of finding additional sources of financing becomes especially topical in order to activate the development of innovative activities in Russia. The mechanism of venture financing and related services can be: loans, credit, leasing, joint (joint) activity, financial investment. State financial institutions ensure the implementation of the state policy to support innovation in priority areas of scientific and technological development by financing innovation projects on preferential terms for the return of provided financing.
The analysis of recent researches and publications. The problems of financing innovative activity and increasing its activity during the last decade are widely studied by modern scientists. Certain aspects of venture investment of innovative projects in Russia and the role of venture capital in this process have been studied by such scientists as G. Birman, S. Schmidt, L.P. Goncharenko, Yu.A. Arutyunov, S.A. Filin, B.T. Kuznetsov, V.N. Sidorova, A.E. Shklyaev, I.R. Fatyanova, S.Yu. Panarina, V.P. Savchuk, K.N. Petrov, and others. Despite the existence of a significant number of publications on this subject, taking into account the current state of the national economy and the need to overcome the consequences of the financial crisis, there is a growing need for further scientific research in this direction.
In our opinion, the issues of the formation of a specific mechanism for financing the activities of local innovation centers have not been solved yet. Methods and instruments of such financing, as well as the mechanisms for the implementation of bank lending, the investment of such centers, their advantages for the subjects of such cooperation need to be specified.
The main goal of the work is to identify alternative ways to activate new venture financing mechanisms for innovation projects in Russia and to identify prospects for further cooperation between local innovation centers and other business entities.
The statement of the main material. The analysis of the world experience of using such forms of activation of innovation activity in the US, Japan, Western Europe, CIS and other countries proves their relevance and prospects for Russia. At the same time, the effectiveness of the functioning of local innovation centers is largely determined by the proper level of financing of their activities, especially at the initial stage.
For working out alternative schemes of financing of local innovative centers, it is expedient to describe this mechanism by the creating special state programs.
When creating such programs, it is useful to take advantage of the experience of the United States as one of the leading countries with an innovative type of economy and the most effective mechanism for the formation of an innovation strategy. Adapting such American programs as the “Innovative Research Program”, “Trans-atmosphere of Technologies” program, “Small Business Technology Transfer Program” and “The Latest Technologies Program” [10] to the Russian conditions for the development of local innovation centers, the authors proposed two new programs: “The program of joint financing of the development of local innovation centers” (based on public-private partnerships), “The cooperation Program – “University – Local Innovation Centers”.
“The program of joint financing of the development of local innovation centers” provides:
1) establishment of the Public-Private Partnership Agency;
2) implementation of co-financing programs for the implementation of:
– joint research and development in important industries for the state;
– transfer of research results to enterprises;
– innovative projects of local innovation centers.
3) creation of venture funds by applying public-private partnership mechanisms and mobilizing public and private financial resources to finance the operation of local innovation centers.
The proposed program provides for strengthening the interrelationships of the state-science-business triangle in the context of the development of local innovation centers. The conception of the program should be based on a harmonious combination of public and private interests. Regulation is due to the optimal balance of regulatory and market levers. At the same time, the role of the state is emphasized:
– in the financing of fundamental science (priority, including its socially important areas);
– in public-private partnerships to mobilize venture financing for private sector investment;
– in the creation of a system of interaction between business and science.
Private business and entrepreneurial initiative should play a leading role. The role of the state in innovative relations are also changing. The state acts in relations not only as a subject of power, but as an equal partner, as an entrepreneur who is ready to share risks from the innovation activity.
“The program of joint financing of the development of local innovation centers” should be implemented at the following levels:
– at the strategic level – The Agency of public-private partnership, which should include representatives of the public and private sectors. The powers of the Agency should primarily include forecasting the needs of the national economy, individual industries from the standpoint of ensuring the technological advantages of their competitive development, selecting innovative projects on a competitive basis, creating or facilitating the creation of new and high-tech industries, information and marketing support for innovation activities;
– at the level of science – local innovative centers (technological parks, industrial parks, science parks, innovation centers, research and development institutions, business incubators) that will assess the innovation ability (market orientation) of scientific research results, qualify innovation objects, assist with accounting and taxation, patent support and registration of intellectual property rights to small innovative firms;
– at the level of the commissioning – commercial partnerships on the basis of research institutions for the purpose of innovation (commercialization of developments) in which public research institutions will enter with intellectual property rights, and private investors with financial contributions;
– at the level of financing – the Innovative Fund for joint public-private investment, which should be created in the form of a private company. It will consist of a holding company and subsidiaries, 50 % of the capital of which is owned by the state, and the rest – to private investors [1].
With the aim of forming effective mechanisms of venture financial support for innovation and economic growth in Russia, it is advisable to introduce a separate structural element within the state financial system – the Innovation Bank. This will help increase the aggregate turnover of venture financing of innovation projects of local innovation centers. The state should own a controlling stake in this bank at the initial stage of activity. Other national co-founders of the bank will be large enterprises and any other interested economic entities, subsequently non-residents of the country.
In order to protect against risk and guarantee the return of private capital to the investor in the event of a risky event, it is advisable to authorize the insurance company chosen by the executive authorities to insure investment in innovation [6]. This company should closely cooperate with all institutional structures, first of all, with the Innovation Bank and the Innovation Fund.
To ensure co-financing, the program uses the following mechanisms:
– Provision of direct loans by the Innovation Bank to those persons who can not avail themselves of the usual channels for attracting credit resources. It will make possible:
– Provision of investment from the Innovation Fund for joint public-private investment in the implementation of those projects that were selected by the Public-Private Partnership Agency. This mechanism provides for the possibility of promoting the development of strategically important developments and areas of scientific research for the country;
– Financial support for residents of industrial parks, who invest in innovation: joint financing of labor remuneration for staff involved in research (50 % financed by the Innovation Fund);
– Joint financing of projects, transfer to industrial production parks with higher added value (up to 40 % is financed from the Innovation Fund). It would increase the attractiveness of Russian industrial parks, open a business case for private investment for the construction and registration of parks in the national registry, and it would stimulate the transfer of more high-tech industries to the country;
– Financing of projects selected on a competitive basis by the Agency of Public-Private Partnership, initiators of creation of local innovation centers: budget financing – 30 % of the project cost, the rest – private companies or local authorities [7].
It is advisable to apply the experience of Israel and the United Kingdom. The share participation of specially created state investment funds in regional venture funds has become a catalyst for the development of venture investment and is already actively being introduced [4]. Both funds are created in the organizational and legal form of a limited partnership, operate under the guidance of private management companies (usually foreign). State funds are usually not more than 50 % of each regional fund, the rest should be attracted from private investors. With regard to payments, the first victim’s rule applies to the benefit of the private investor [2].
The general scheme of interaction of subjects on the “The program of joint financing of the development of local innovation centers” is presented in Fig. 1.
The advantages of this mechanism are: firstly, for business it is direct state support of innovations and the possibility of investing under state guarantees; secondly, for the state, this is a reduction in budget expenditures due to raised funds in the sphere of innovation, an increase in the innovative activity of priority sectors of the economy and the distribution of innovative risks.
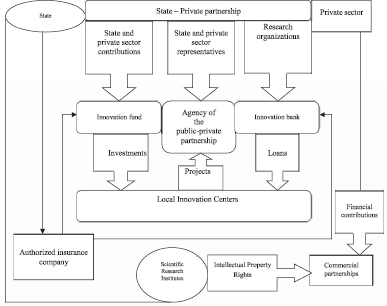
Fig. 1. The general scheme of interaction of subjects under “The program of joint financing of the development of local innovation centers”
“The cooperation Program – “University – Local Innovation Centers” is aimed at bridging the gap between education and the introduction of knowledge in the creation of innovations. Within the framework of this program, two basic programs are key: the programs of joint research centers “university-industry” and the program of creating youth innovation centers. When creating the first program, it is advisable to take the US experience as a prototype.
Along with strategic business alliances, the university-industry partnership has been actively developed over the last 30 years in the United States. Financing in such cases is carried out on a contract basis, and the owner of the research results is a financing company. The system “university-industry” has become so widespread that in many educational institutions special centers (more than 1000 throughout the USA) were established that serve such projects [3]. In our opinion, the stimulation of such cooperation contributes to the acceleration of the emergence of various types of local innovation centers (LIC) by combining the innovative potential of education and commercial progress, and therefore, the commercialization of innovation as the achievement of the goal of creating LIC.
The program of joint research “university-industry” centers provides for two options for funding mechanisms for such centers. The first option is based on the formation of a research center in the form of a corporation, which may include universities, private investors, local authorities, other sponsors and stakeholders. Each corporate member of the Center contributes an annual fixed membership fee to the general fund. This contribution is directed to financing of fundamental research, the themes of which are determined by the Council of the Center.
The next stage is the introduction of scientific developments in production by creating a spin-off company [5]. In case of its successful functioning, the Center’s fund should distribute the revenues received among the participants. Universities and institutions need to report on revenues from licensing, investments from outside investors in research and development and spin-off companies, income from spin-off activities, the number of jobs created or developed social products to the Council of the Center. The basic scheme of the functioning mechanism of the University-Industry Research Center in the form of a corporation is presented in Fig. 2.
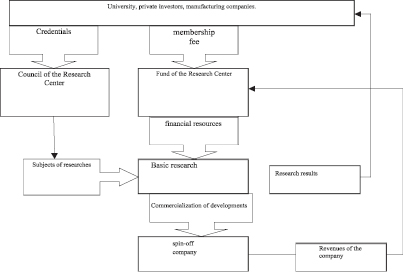
Fig. 2. The basic scheme of the functioning mechanism of the “University-Industry” Research Center in the form of a corporation. Source: developed by the authors on the basis of sources [8, 9]
The second option involves participation in the financing of an innovative non-banking financial and credit institution “Small Innovation Business Support Fund”. The Small Innovation Business Support Fund provides relatively small financial support to the centers – 20 % [10]. At the same time, 80 % of financing comes from other industrial companies. If the center can prove its ability to carry out serious research, the Small Innovative Business Support Fund provides a grant for five years, which can be extended for another five years, but for a smaller amount. The aim is to help start the work of the center, as well as support at the stage of formation, but in future the centers should be supported by universities and industry.
The partnership of the parties in the center is formalized through the adoption of joint decisions by the Consultative Industrial Council of the Center, representatives of the university and the business of carrying out scientific research. Indicator of success according to the criteria of the Fund, should be the volume of research carried out by the Center on contracts with industry.
It is also determined that an important task for the state is to search for promising ideas in universities and research centers, ensure investment financing in the early stages of the development of companies, finance the development of business plans and research activities, expand international cooperation of research organizations.
To ensure funding, the following mechanisms can be applied:
– financing of projects at the level of up to 30 % through direct subsidies;
– the allocation of grants of the company to half of the costs, if it does not only develop a new product, but also research in cooperation with the university;
– the allocation of risky loans to the company up to 60-70 % of the cost to develop a new product or process. The company is obliged to repay the loan if the development was successfully introduced into the market;
– financing of projects for a period of up to two years, and in case of favorable results of the development of a new product is extended for another 2-3 years in the form of a risk loan. Such measures can be entrusted to the Fund for Support of Small Innovation Business, since it does not contradict its charter and the goals of creation.
Conclusions and offers. The proposed measures to improve the mechanisms of venture financing of innovation projects in Russia and the financial support of local innovation centers are implemented through two state programs. These programs provide for a combination in a single system of interaction: local innovation centers, financial and credit institutions, industrial enterprises, higher education institutions and private investors through indirect instruments of the state influence. The implementation of these programs will ensure the transition of the economy to a new innovative level, will promote positive changes in the field of education, increase employment of the population and, as a result, will enhance the development of the national economy as a whole.

