Традиционные методы лечения проблемной кожи имеют хирургическую, физическую или химическую природу, но все перечисленные методы имеют побочные эффекты, особенно если они сопровождаются рубцеванием. Современный этап развития комбустиологии, косметологии, пластической хирургии, транспланталонии характеризуются отсутствием фундаментальных основ и представлений для проведения запрограммированных управляемых эффективных методов лечения с избеганием риска осложнений, которые надежно остановили бы прогрессирование патологического рубца и его рецидивы после хирургического лечения. Современные технологии не инвазивного метода в области косметологии и эстетической медицины позволяют усиливать эффект обновления в после операционный период и по окончании курса лечения помогают длительно сохранить достигнутый результат. Причиной отсутствия возможности индукции направленной регенерации кожи является недостаточная изученность процесса репаративной регенерации как после ожогов, так и после оперативных вмешательств на коже, что диктует необходимость более глубокого изучения механизмов заживления ран. Более глубокий уровень изучения процессов повреждения и старения кожи окажет несравненный толчок в изучении методов омоложения кожи и позволит активизировать процесс их внедрения в медицинскую практику для дальнейшего применения.
1. Jinnin M, Yamamoto T, Asano Y, Ishikawa O, Sato S, Takehara K, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Ihn H. Diagnostic criteria, severity classification and guidelines of eosinophilic fasciitis. J Dermatol. 2018 Aug;45(8):881-890. DOI: 10.1111/1346-8138.14160. Epub 2017 Dec 13.
2. Golberg A, Khan S, Belov V, Quinn KP, Albadawi H, Felix Broelsch G, Watkins MT, Georgakoudi I, Papisov M, Mihm MC Jr, Austen WG Jr, Yarmush ML. Skin rejuvenation with non-invasive pulsed electric fields.//Sci Rep. 2015 May 12;5:10187. DOI: 10.1038/srep10187.
3. Meneghetti KL, do Canto Canabarro M, Otton LM, Dos Santos Hain T, Geimba MP, Corção G. Bacterial contamination of human skin allografts and antimicrobial resistance: a skin bank problem. BMC Microbiol. 2018 Sep 24;18(1):121. DOI: 10.1186/s12866-018-1261-1.
4. Mathieu D, Marroni A, Kot J. Tenth European Consensus Conference on Hyperbaric Medicine: recommendations for accepted and non-accepted clinical indications and practice of hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Diving Hyperb Med. 2017 Mar;47(1):24-32. DOI: 10.28920/dhm47.1.24-32.
5. Jović MS, Dimitrijević MM, Dimitrijević AM, Stojković GG. Analysis of reconstructive methods in surgical treatment of nasal skin defects. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2016 Aug;73(8):723-7. DOI: 10.2298/VSP140829052J.
6. Tam KW, Lai JH, Chen HC, Hou WH, Ko WS, Chen SL, Huang TW. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing interventions for peristomal skin care. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2014 Oct;60(10):26-33.
7. Longobardi P, Hoxha K, Bennett MH. Is there a role for hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the treatment of refractory wounds of rare etiology? Diving Hyperb Med. 2019 Sep 30;49(3):216-224. DOI: 10.28920/dhm49.3.216-224.
8. Yi J., Hong T., Zeng H., Li P., Li P., Wang S., Chen J., Li P., Zhou J. A Meta-analysis-Based Assessment of Intense Pulsed Light for Treatment of Melasma. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2020 Jun;44(3):947-952. DOI: 10.1007/s00266-020-01637-x.
9. Tatlıparmak A, Aksoy B, Shishehgarkhaneh LR, Gökdemir G, Koç E. Use of combined fractional carbon dioxide laser and fractional microneedle radiofrequency for the treatment of acne scars: A retrospective analysis of 1-month treatment outcome on scar severity and patient satisfaction. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020 Jan;19(1):115-121. DOI: 10.1111/jocd.13004.
10. Buzzella A, Mazzini G, Vicini R, Angelinetta C, Pastoris O. A preliminary study of an alternative method for evaluating skin sensitizing potential of chemicals. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019 Jun;41(3):257-264. DOI: 10.1111/ics.12530. PMID: 30993720.
11. Philipp-Dormston W.G. Photodynamic therapy for aesthetic-cosmetic indications // G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Dec; 153(6):817-826. DOI: 10.23736/S0392-0488.18.05982-5.
As an organ, the skin makes up 15-20 % of the human body weight. Nowadays, significant attention is paid to skin aesthetics, which led to the emergence and development, in addition to traditional medical cosmetology, of such areas as aesthetic and plastic skin surgery, surgical cosmetology and others. The development of these areas required a new level of knowledge about the functional morphology of the skin, its changes under various surgical procedures with the very purpose of maintaining its aesthetic appeal and healthy state for a long time.
Purpose of research
Choose a method of applying the effectiveness and safety of non-invasive skin rejuvenation. To select individually the best method of non-invasive treatment of problem skin, which will be the most accessible and applicable to a wider range of age patients who need aesthetic correction and patients with skin problems not only of an age nature, but also after burns, removal of neoplasms, skin transplantation due to traumatic and post-burn defects.
Material and methods
For the period 2015-2019, materials from the literature on aesthetic correction of skin defects and age-related cosmetology, as well as data from clinical practice, were taken as the basis for studying the effectiveness of a non-invasive technique. The clinical material was obtained in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (2000) and the 2013 amendments with the permission of the FEFU Ethics Committee.
Results of analysis of literature data
The skin is the organ with the greatest susceptibility to environmental factors. Thermal and chemical factors, electricity occupy the most leading places among these factors. The appearance of scars often causes serious functional, cosmetic disorders, disability of patients, a decrease in the quality of life of patients, psychological problems arise, which requires long-term specialized treatment. Currently, there are no generally accepted algorithms for choosing methods for preventing the development and treatment of scars, and the tactics of treating patients with scars are most often based on the personal experience of practicing doctors. The development of such algorithms is difficult due to the uncertainty of the terminology, the inconsistency of the criteria for the differential diagnosis of various types of scars, insufficient evidence of scar treatment methods. This is due to the fact that most of the studies are subjective, as well as with a long period of scar tissue formation, which complicates the observation of patients.
The current literature, against the background of the numerous methods for treating skin lesions, there is no analysis of data on monitoring the consequences, long-term outcomes and results of the treatment performed when using various methods, which complicates the development of recommendations for choosing a treatment for problem skin [1].
1. One of the new non-invasive, non-thermal methods of treating problem skin is the method of exposure using pulsed electric fields. Golberg A., Khan S., Belov V. (2015) developed a methodology and successfully proved the use of pulsed electric fields in rats, which led to a noticeable proliferation of the epidermis, the formation of microvessels and the secretion of new collagen in the treated areas without scarring.
The results show that pulsed electric fields can serve as a new non-invasive skin therapy for multiple degenerative skin diseases [2].
2. Pain is a common side effect of dermatological laser procedures (resurfacing for rejuvenation, removal of age spots, hair removal, leg telangiectasia, facial telangiectasia, removal of tattoo marks, removal of papillomas due to HPV lesions), therefore, for the effectiveness of treatment, it is necessary to use non-invasive anesthetics and anesthetic procedures. Use of local anesthetics or skin cooling is allowed. It is necessary to consider nationality- and sex-based statistically significant differences in pain perception, women are easier to tolerate the pain. Local anesthetics effectively increase pain threshold than the skin cooling. All these data can be recommended for everyday clinical practice [3].
3. The use of radiofrequency radiation with multiple sources, combining 3 different methods for the patient: non-ablative radiofrequency skin tightening, fractional skin resurfacing, and the use of RF-microneedles for non-ablative coagulation and collagen remodeling [4].
4. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a method of treating various dermatological diseases, including actinic keratosis. There are two types of PDT available, the traditional PDT (c-PDT) and the newly developed day PDT (DL-PDT). Both methods require a local photosensitizer, light source, and oxygen, and are comparable in efficacy for the treatment of photoinduced skin aging. The treatment is effective in eliminating fine wrinkles, skin roughness, actinic elastosis and macular hyperpigmentation. The most effective PDTs are 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and methyl aminolevulinate (MAL). Several pre-treatments help improve the absorption of the photosensitizer by the skin and result in a significant increase in effectiveness. The main limitation of c-PDT is the significant pain associated with treatment, but DL-PDT has proven to be almost painless. The duration of the treatment is 2-3 treatment cycles, and the results are completely obvious in 3-6 months after the treatment. The unique advantage of PDT is that it is a non-invasive procedure that effectively treats a range of dermatological conditions, including the prevention and therapy of precancerous actinic keratosis [5].
5. It was noted that a statistically significant improvement in the skin was observed in those patients who received non-invasive application of vitamin C. At the same time, rejuvenation was observed from the side of a decrease in the indicators of photoaging of the cheeks and perioral region (P = 0.01), the periorbital region, which is associated with improved hydration. The biopsy showed an increase in collagen as well as enhanced mRNA staining for type I collagen and no evidence of inflammation [6].
6. Extracellular matrix (ECM), comprising of more than 70 % of skin, is the major node of skin recovery and regeneration. ECM is a unique therapy used in sports medicine cosmetology for pain relief. It consists in the accumulation of collagen fragments and agglutination of amorphous elastin. Chronic skin aging treatment requires preparation of the skin bed to optimize the results of rejuvenation procedures and skin care programs. This includes the application of agents, which are matrixins, peptides resulting from the fragmentation of matrix proteins that exhibit a wide range of biological activities. Emerging cosmetic and functional defects that cause psychological discomfort to the patient, impaired active social adaptation of patients after injuries and operations that significantly affect the quality of life, high probability and risk of developing cancer against the background of scarring after burns, the relevance of studying the features of skin alteration and regeneration in case of injuries of various etiologies is extremely high [7]. Yi J., Hong T., Zeng H., Li P., (2020) believe that there are still complex clinical problems associated with the lack of effective treatment regimens with targeted control of the skin regeneration process after burns and autodermotransplantation in the wound area. At the present stage, the reasons why some keloids arise from a mature scar several years after the initiating injury are unknown, there is no data and monitoring of the methods used to treat skin problems in the patient’s history [8]. Also, the reasons for the development of true keloid disease are not clear (Fig. 1, 2).
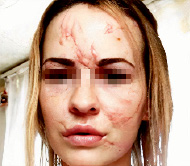
Fig. 1. Keloid scars of a 25-year-old woman
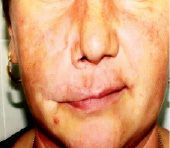
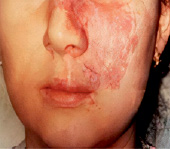
a b
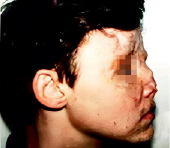
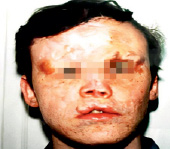
c d
Fig. 2. Scars of the facial skin after burns of a 58-year-old woman (a); facial scars after burns of a 25-year-old woman (b); facial scars of a 34-year-old man after injury (c, d)
7. Bioxytherapy is a technology in which oxygen is supplied under pressure to the skin, the concentration of which is about 90 %, which is significantly higher than in the atmosphere (21 %). The cells of the surface layer of the skin receive oxygen under the influence of pressure, thereby increasing the metabolic rate in the epidermis and dermis. At the same time, the permeability of the skin increases, which enhances the effect of the active components that make up the cosmetic preparations used during the procedure [9]. The permeability of the intercellular membrane increases, the absorption of the active substances of the preparations increases, which even after the procedure nourish and protect the skin for a long time. In most cases, the effect is visible to the naked eye immediately after the first oxygen needle procedure: the skin acquires a smoother shade and smoother texture. Multiple deep moisturizing and skin rejuvenation procedures eliminate flabbiness and dryness of the skin, refresh and tone it. Non-injection wrinkle filling procedures smooth out fine wrinkles and reduce the severity of deeper ones, effectively treat puffiness and dark circles under the eyes, increase skin elasticity and restore a youthful, healthy complexion. The result extends not only to the skin, which after each procedure becomes more even and taut, the complexion improves. After the procedure, the skin will look healthy and fresh. The metabolism is normalized, the skin regeneration processes are accelerated. Immunity increases, the general condition of the body improves [10]. Bioxytherapy can also be carried out for the prevention and treatment of various post-traumatic conditions, long-term non-healing damage to the skin, overwork, and environmental chronic stress. It is also recommended for young skin to improve the results of cleansing, as well as to combat dryness, dehydration, skin stress, the effects of lack of sleep, and prevent the first wrinkles. Also, oxygen therapy procedures give excellent results in the treatment of problem skin, in the complex therapy of superficial hyperpigmentation. There are no contraindications to this procedure, no complications have been identified. Oxygen mesotherapy is completely painless, the skin surface remains intact after treatment [11].
Conclusion
There are many different skin rejuvenation techniques available, but pain is a common side effect of these procedures, which can be relieved by local anesthetics or cooling.
In contrast to invasive, non-invasive techniques imply a more gentle, delicate effect on the skin, completely eliminating penetrating trauma to the epidermis. Thus, when using them, the skin remains completely intact and unharmed. The advantages of non-invasive anti-aging methods over invasive ones are obvious. Due to the absence of skin trauma during these procedures, patients do not experience pain. These methods have fewer contraindications compared to invasive methods of rejuvenation. Complications, if a specialist adheres to the technique of the procedure, are also rare. It takes little time to complete the anti-aging measures, the recovery period is either minimal or absent altogether, there is no danger of infection. In addition, the choice of non-invasive methods of rejuvenation is much wider than the range of invasive methods for correcting age-related changes, and they also give a rather long-term effect, calculated for years. In addition, after a non-invasive intervention, the body continues for a long time to independently synthesize substances that contribute to the preservation of youth and health of the facial skin.
The study was financially supported by the International Medical Research and Education Center (Vladivostok, Russia).
Scientific advisers – MD, Professor Reva G.V., Professor Gulkov A.N.
Библиографическая ссылка
Рева Г.В., Бессонов Е.А., Ленда И.В., Пономарев А.В., Ковалева И.В. АНАЛИЗ МЕТОДОВ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ ПРОБЛЕМНОЙ КОЖИ // European Journal of Natural History. 2021. № 3. С. 29-32;URL: https://world-science.ru/ru/article/view?id=34182 (дата обращения: 08.01.2026).

