The purpose of the research is to study specific features of bilingual sphere medical university e-learning. The e-learning basic elements in medical school foreign students’ educational process were considered as the research object. Research methods: supervision, reflection, analysis, questioning, interview. Material. Results of first-year foreign students’ testing served as material of our research. In total 244 first-year students of Kursk state medical university were interviewed. Examinees studying medicine in English were grouped according to the rate of academic progress. Results. Medical university foreign students’ demands of e-learning basic elements in educational process are analyzed in the article. Advantages and limitations of e-learning basic elements in bilingual sphere of medical university are studied, problem of e-learning usage in complex with university traditional methods of teaching is considered. The aspect of e-learning effectiveness in international students’ cultural and professional competence formation is studied with respect of examinees educational activity.
E-learning is defined by UNESCO as students’ education based on internet and multimedia technologies. Pedagogical research results proof that university e-learning stimulates students’ cognitive activity [2, 5], improves their educational results [4, 6], allows to use modern science and technology achievements in educational process, optimizes process of independent work [3] and provides effective students’ self-control. At the same time it should be noted that specific features of bilingual sphere university e-learning are a little investigated [1] in spite of the fact that relevance and demand of such works are extremely high as:
– firstly, universities of Russian Federation at present are accepting the considerable number of foreign students to study in intermediate language as English most often acts.
– secondly, owing the fact that high school e-learning various elements are actively used in educational process of international faculty students differing basically on scientific knowledge, language skills and cultural background.
In this regard the purpose of the research is determined as specific features studying of bilingual sphere medical university e-learning. The e-learning basic elements in medical school foreign students’ educational process were considered as the research object.
Material and methods. Results of first-year foreign students’ testing served as material of our research. In total 244 first-year students of Kursk state medical university were interviewed. Examinees studying medicine in English were grouped according to the rate of academic progress: 27 % of all students were included into the group with high results of educational activity, 70 % – into the group of average academic rate, and 3 % of all students were in the group with poor educational results. The experiment was held in constant conditions for all groups of students: the research was held at 11 a.m. in the academic auditory. The research duration was about 12 minutes. The medical faculty students performed the testing independently. The testing was built on the basis of original author test including 12 questions.
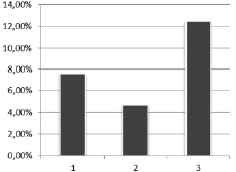
Fig. 1. Number of first-year foreign students that esteems multimedia lectures as ineffective element of medical school educational process. Note: 1 – high educational rate students (4,7 %); 2 – average educational rate students (7,6 %); 3 – low educational rate students (12,5 %)
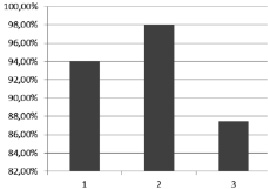
Fig. 2. Number of first-year foreign students that considered educational computer tasks as effective medical school educational component. Note: 1 – high educational rate students (94,0 %); 2 – average educational rate students (98,2 %); 3 – low educational rate students (87,5 %)
Results. At the initial stage of the research examinees studying medicine were asked to arrange the e-learning basic elements according to the frequency of their use in university educational process. international faculty students put e-learning elements in the following order:
– multimedia lectures;
– electronic manuals;
– computer testing;
– laboratory works on the computer;
– problem tasks on the computer;
– university website information.
Next stage of the research the examinees started to esteem the effectiveness of e-learning elements. According to the research results multimedia lectures are considered by 91,8 % of first-year foreign students as useful component of medical school educational process (fig. 1).
However, 4,7 % of students with good results of studying, 7,6 % foreigners with high academic rate and 12,5 % first-year students with poor educational activity results esteem multimedia lectures as ineffective. For comparison: to the opinion of 100 % of domestic students with low academic rate multimedia lectures is irreplaceable component of university educational process, the great instrument of representing and visualizing the information. To our mind, the fact that low educational rate foreign students do not appreciate the value of multimedia lectures in university educational process can be explained by difference in basic scientific knowledge, namely in computer skills, between foreign students. If Brazil and Malaysia representatives masterfully use modern computer technologies, students from India and Sri Lanka experience serious difficulties in computer usage. Students admit the fact that e-learning is unusual for them, and causes rejection at first. Fidelity of our thought is also confirmed by foreign students’ testing results in the question about educational computer task expediency. Educational computer tasks are considered as effective medical school educational component by 96,7 % of international faculty students: by 94 % of students with high rates of the academic progress, by 98,2 % of students with good results of studying and by 87,5 % of students with poor educational results (fig. 2).
Computer tasks are difficult for the first-year students with low results of educational activity, because they do not have enough knowledge in software and computer technologies. Exactly the same difficulties low academic rate students face in computer laboratory works performing. They are considered as inefficient by 11,5 % of poor educational results students. Computer testing is considered effective by 91 % of international faculty students. 100 % of students with low academic rate expressed opinion of sufficient objectivity of computer testing results. To our mind, definite algorithm of testing programs does not cause rejection by foreign students. The accurate test questions formulation, computer testing programs option of choosing between possible answers removes a linguistic barrier, eliminates psychological discomfort of foreign students. Summarizing all that has been said, it should be definitely noted that there are some specific features of e-learning in bilingual sphere. E-learning first of all is demanded by high academic rate foreign students, and it frightens off students of international faculty with poor educational results because its novelty. Insufficient base of computer knowledge does not allow foreign students with low results of educational activity to be completely included into e-learning process.
In our opinion, such measures as accurate algorithmization of work, gradual introduction of new e-learning elements, the main attention to computer testing, detailed explanations of electronic manuals usage promote ensuring psychological comfort of foreign students, formation of positive reaction of international faculty students to e-learning , will allow the international faculty students to take all the advantages of e-learning.
Библиографическая ссылка
Snegireva L.V. SPECIFIC FEATURES OF BILINGUAL SPHERE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY E-LEARNING // European Journal of Natural History. 2017. № 2. С. 31-33;URL: https://world-science.ru/ru/article/view?id=33721 (дата обращения: 13.03.2026).

