The market situation is changing at every stage of the life cycle and requires a corresponding change in the strategy and tactics of enterprise activity in the market that is of particular importance.
The main products have 4-5 stages, before disappearing from the market:
- Presentation (launch);
- Growth (development);
- Maturity (stabilization);
- Decline (decline and updating products);
- Death (death and the start of goods relaunch cycle).
A product life cycle depends on the number of substitutes, their competitiveness, as well as on the right management decisions aimed at developing supporting activities to optimize the structure of the product life cycle. The main activities to optimize the structure of the product life cycle include: proper use of various elements of marketing at various stages of product life cycle; production strategy of the enterprise.
A footwear manufacturer must plan his production strategy, based on the possibility to use marketing elements to optimize the structure of the product life cycle.
Different companies take different approaches to devising the strategy of goods production depending on customer needs, available resources, market conditions, etc. Moreover, the same company can use different strategies for different goods. The strategy selection is usually based on the product competitiveness.
The development of new combinations of goods is based on targets and strategies of enterprises and is accompanied by the analysis of the enterprise position, resulted in making a decision on the probable diversification of its activities. The consideration of the factors that are controlled by marketing (Figure 1), as well as the factors that are not controlled by marketing (Figure 2) is a prerequisite for the strategy devising.
Thus, the product life cycle management is the process of product management from the product concept to its utilization. When this process is efficient, the enterprise is able to operate profitable innovations, to accelerate the development of new products, to launch them shortly and constantly improve their quality, while reducing their production costs.
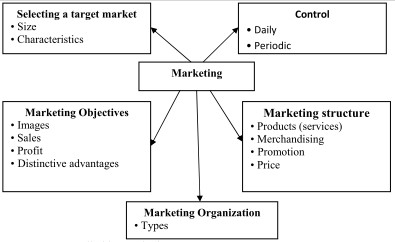
Figure 1. Factors controlled by marketing
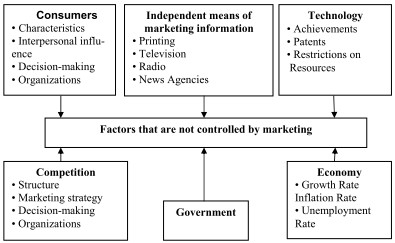
Figure 2. Factors uncontrolled by marketing
Five stages in the footwear life cycle require permanent change of pricing strategy. A product life cycle is characterized by fluctuations in sales and profits from its sale. Thereafter, the price will vary depending on what stage of life cycle the goods are at. Thus, we can conclude that the price set by the enterprise for the goods depends on the production costs, supply and demand, as well as the population solvency, pricing and market strategy of the enterprise, product quality, interchangeability of goods and their life cycle.

